Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that act on cannabinoid receptors present in the human body, as well as in the bodies of other mammals.
Depending on their origin, they can be classified into:
- Phytocannabinoids
These are compounds that are found only in nature in the plant. The plant is only capable of synthesizing them in their non-psychoactive acidic forms, the main ones being THCA, CBDA, CBGA, CBCA. Acidic substances transform into active neutral substances under the influence of heat or light.
- Endocannabinoids
They are produced by almost all organisms in the animal kingdom and bind to the body’s cannabinoid receptors, this communication is the endocannabinoid system. The main ones are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, and the primary receptors in the body are CB1, mainly located in the central nervous systems, and CB2, mainly located in the immune system.
- Neocannabinoids
These are compounds generated in the laboratory. Two examples with therapeutic properties are nabilone and nabiximols.
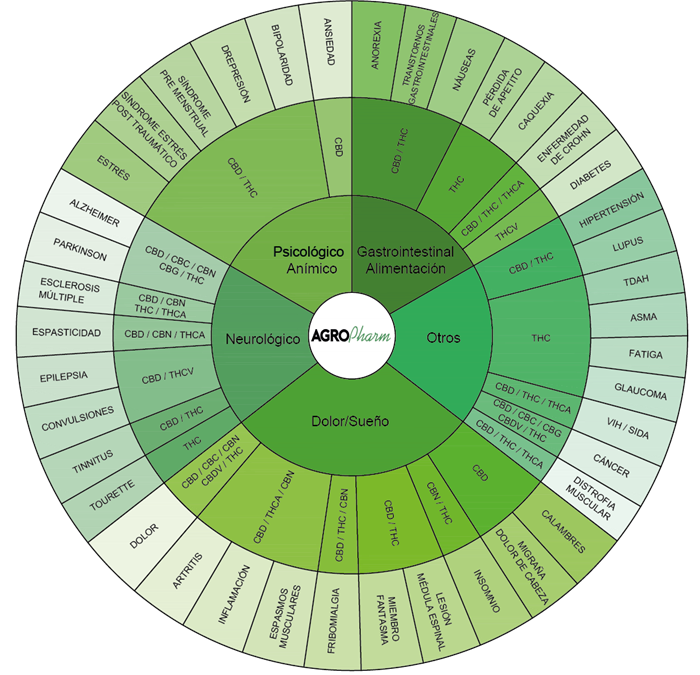
Evaluating cannabinoids based on your profile can help you better identify cannabis for your symptoms.
Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid (THCA)
It is the primary component of fresh cannabis. THCA transforms into THC when heated to an appropriate temperature. It contributes to anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, and antispasmodic effects.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
It is the most abundant cannabinoid in the cannabis plant, responsible for the well-known psychoactive effects, while its acidic form is non-psychoactive. It has a mild analgesic effect and has demonstrated antioxidant activity.
Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA)
Similar to THCA, CBDA is the primary component of cannabis with high levels of CBD. CBDA contributes to anti-inflammatory effects.
Cannabidiol (CBD)
CBD has significant medical potential, especially when the right ratio of CBD to THC is used to treat a specific condition.
Cannabinol (CBN)
CBN is a moderately psychoactive cannabinoid produced from the degradation of THC. The degradation of THC into CBN results in a sedative effect known as “Couch Lock”.
Cannabigerol (CBG)
CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid. It may eradicate or slow bacterial growth, reduce inflammation (especially in its acidic form CBGA), inhibit the cell growth of cancerous/tumoral cells, and stimulate bone growth.
Cannabichromene (CBC)
CBC is more common in tropical varieties of cannabis. It may alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, inhibit the cell growth of cancerous/tumoral cells, and stimulate bone growth.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
THCV is present in low concentrations exclusively in some cannabis varieties. Its effects include a reduction in panic attacks, appetite suppression, and stimulation of bone growth.
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
Similar to THCV, CBDV differs from CBD and shows promise in the treatment of epilepsy.
*NOTE: Our information is based on scientific studies or outreach; if you are considering using cannabis, please consult with a specialized medical professional.